When seeking financing, many borrowers may be required to provide collateral to secure a loan. Collateral serves as a safety net for lenders, reducing their risk and potentially allowing borrowers to access larger amounts or better terms. Understanding the intricacies of using collateral is essential for anyone considering obtaining a loan, be it for personal use, business ventures, or real estate investments.
In this article, we will delve into what collateral is, the types commonly used, the benefits and risks associated with using collateral for loans, and factors to consider before proceeding. By the end of this exploration, you should have a clearer picture of how collateral functions within the lending landscape and how to navigate its complexities effectively.
What is Collateral?

Collateral is an asset that a borrower offers to a lender to secure a loan. It acts as a form of guarantee that the lender can claim if the borrower defaults on their loan obligations. This mitigates the lender's risk and can sometimes result in more favorable loan conditions for the borrower.
Assets typically used as collateral can vary widely, ranging from tangible property to financial instruments. Understanding the nature and value of collateral is crucial for borrowers to make informed decisions when securing a loan.
- Real estate (homes, land)
- Vehicles (cars, boats, motorcycles)
- Savings accounts
- Investment accounts (stocks, bonds)
- Equipment and machinery for businesses
- Personal property (jewelry, artwork)
The use of collateral is a common practice in various financing scenarios, allowing both the lender and borrower to engage in a more secure transaction. However, it's vital for the borrower to understand the implications before putting their assets on the line.
Common Types of Collateral

Different types of collateral can be utilized based on the nature of the loan and the value of the asset. Understanding the most common types can help borrowers identify what assets they possess that may serve as effective collateral.
- Real estate properties
- Vehicles such as cars and motorcycles
- Cash deposits and savings accounts
- Marketable securities like stocks and bonds
- Valuable personal property (jewelry, art)
Choosing the right type of collateral can significantly impact the terms of the loan, including interest rates and payment terms. Borrowers should assess their options carefully and consider the associated risks with each type of asset.
Benefits of Using Collateral for a Loan
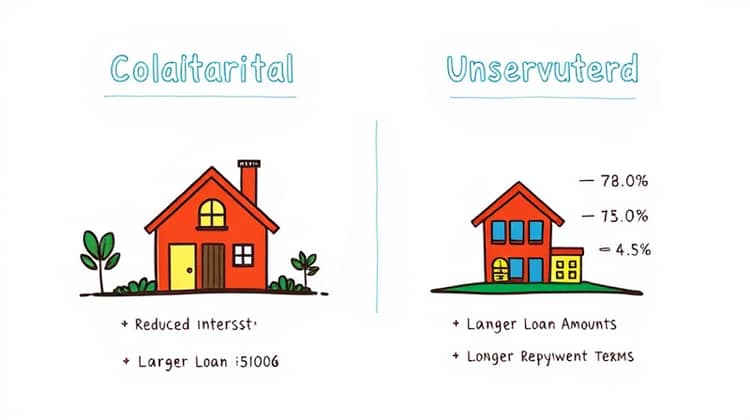
Utilizing collateral when applying for a loan can offer several benefits to the borrower. First and foremost, it can lead to reduced interest rates compared to unsecured loans. Since the lender has a form of security, they face less risk, which often translates into cost savings for the borrower.
Additionally, collateral can enable borrowers to access larger loan amounts or longer repayment terms. This increased access can be especially beneficial for significant purchases such as a home or business investments that might otherwise be unattainable without sufficient credit history.
- Lower interest rates due to reduced lender risk
- Increased borrowing capacity
- Potential for longer repayment terms
- Possibility of improved loan approval chances
- Flexibility in terms of loan types available
Overall, the strategic use of collateral can facilitate financial undertakings that align with the borrower's needs and capabilities.
Risks Involved in Using Collateral

While there are many advantages to using collateral, there are also significant risks that borrowers must consider. The primary risk is the potential loss of the asset used as collateral if the borrower defaults on the loan. This can have devastating financial consequences.
Moreover, the value of collateral can fluctuate, which may lead to issues if the market value decreases significantly below the outstanding loan amount.
- Risk of losing the collateral if payments are missed
- Fluctuations in asset value that may lead to under-collateralization
- Increased borrowing costs if collateral value decreases
- Impact on credit score if payments are not met
Because of these risks, borrowers should thoroughly assess their ability to repay and the implications of putting their assets at risk before securing a loan with collateral.
Factors to Consider When Using Collateral
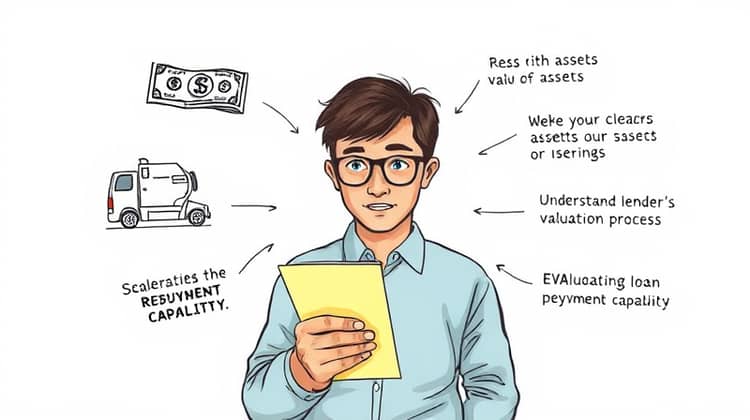
Before committing to using collateral for a loan, borrowers should evaluate several crucial factors. Their current financial situation, the specific terms of the loan, and the implications of using their assets must be well-considered. This careful evaluation can help borrowers make informed decisions that align with their long-term financial goals.
Additionally, it's important to understand the lender's requirements regarding the valuation and documentation of collateral. Knowing how the lender will assess the collateral value can save borrowers from unforeseen complications down the line.
- Assess the value and liquidity of the collateral asset
- Understand the lender's valuation process
- Consider the potential for asset depreciation
- Evaluate your loan repayment capability
- Examine alternative financing options
- Think about the impact on personal finance goals
Taking these factors into account will help borrowers navigate their loan options effectively and minimize potential risks associated with using collateral.
Conclusion

In conclusion, using collateral for a loan can be a double-edged sword. On one hand, it can provide borrowers with access to financing opportunities that may not otherwise be available. On the other hand, it involves risks, particularly the potential loss of valuable assets if loan obligations are not met.
Understanding the various types of collateral, their associated benefits, and the risks involved is imperative for making informed lending decisions. Borrowers should take the time to analyze their assets and understanding their financial position before proceeding with any loan agreements that require collateral.
As with all financial decisions, careful consideration and planning can lead to better outcomes. Ultimately, being well-informed about collateral and approaching the lending process strategically will empower borrowers to take charge of their financial futures.