In the realm of business loans, understanding the nuances of loan covenants is crucial for both lenders and borrowers. Loan covenants act as a safeguard, ensuring that the borrower adheres to certain prescribed standards and behaviors, which ultimately bolster the lender’s confidence in the repayment of the loan. This article delves into the nature, types, and implications of loan covenants, along with strategies for negotiation.
A detailed examination of loan covenants can illuminate their role in business finance. These agreements are not merely rules; they form the backbone of the lender-borrower relationship by setting expectations and providing transparency. Failing to comply with these covenants can lead to severe repercussions, making it essential for businesses to grasp their importance fully.
In the following sections, we will explore various aspects of loan covenants, including their types, purposes, common practices in business loans, and the impact of breaking such agreements. Each facet reveals the critical role covenants play in ensuring the sustainability of financial arrangements, protecting interests on both sides.
What Are Loan Covenants?

Loan covenants are formal agreements between lenders and borrowers that outline specific prerequisites and behavioral expectations that the borrower must adhere to throughout the duration of the loan. By specifying these requirements, lenders aim to control risks associated with lending, ensuring that their investment remains secure. Additionally, these covenants provide a framework for accountability, reducing the likelihood of default.
The terms of loan covenants can vary significantly depending on the type of loan and the financial standing of the borrower. While some covenants might focus on financial metrics, such as debt-to-equity ratios, others may impose operational limits, preventing borrowers from making drastic changes in their business strategy without lender approval. This ensures that the borrower maintains a steady course toward repaying their debts.
It is important to note that loan covenants can generally be classified into two main categories: affirmative covenants and negative covenants. Affirmative covenants require the borrower to take certain actions, whereas negative covenants restrict borrowers from engaging in specific activities. The balance between these two types of covenants underpins many lending agreements.
Types of Loan Covenants
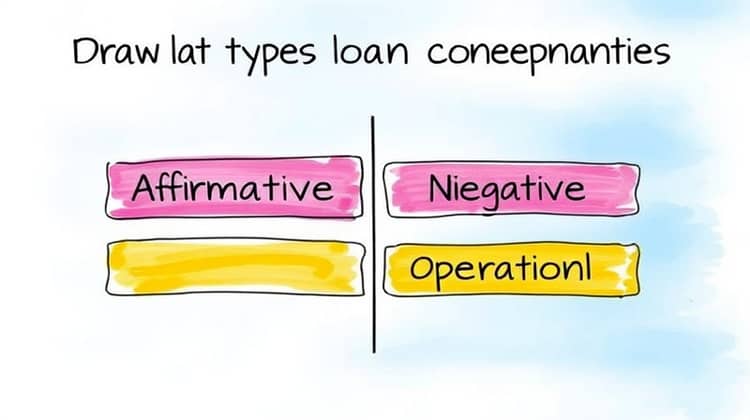
Understanding the different types of loan covenants is essential for both lenders and borrowers to navigate their financial obligations effectively.
- Affirmative Covenants: These covenants require the borrower to perform certain actions, such as providing regular financial reports to the lender or maintaining specific insurance coverage.
- Negative Covenants: These restrict the borrower from taking certain actions, like incurring additional debt or selling substantial assets, without lender consent.
- Financial Covenants: These measures are focused on the financial health of the borrower, stipulating minimum performance thresholds, such as maintaining a certain debt-to-equity ratio.
- Operational Covenants: These covenants monitor the operational aspects of a business, ensuring that borrowers maintain a defined business strategy and adhere to established metrics.
Comprehending these types of covenants can empower borrowers to operate within the expectations set forth by their lenders, thus safeguarding their financial health.
The Purpose of Loan Covenants

Loan covenants serve multiple purposes in the context of business loans. Primarily, they represent an agreement designed to protect lenders by ensuring that borrowers operate within predefined limits. By determining acceptable financial ratios and operational strategies, lenders can mitigate their risk, thereby enhancing the likelihood of loan repayment.
Another key purpose lies in the establishment of trust and accountability between lenders and borrowers. When borrowers agree to covenants, they signify their commitment to transparency and financial responsibility, paving the way for more substantial financial support in the future.
Moreover, loan covenants encourage borrowers to adhere to sensible financial practices, fostering a disciplined approach to debt management. This is particularly important for businesses looking to sustain long-term growth while managing financial obligations.
- Protect Lenders: By setting operating and financial benchmarks, covenants help secure the lender's investment and reduce the risk of default.
- Promote Transparency: Covenants foster an environment of openness between borrowers and borrowers, paving the way for better overall communication.
- Encourage Good Practices: Covenants guide businesses toward prudent financial behaviors, positively influencing their long-term viability.
Thus, the multifaceted purposes of loan covenants contribute to healthier financial ecosystems for both borrowers and lenders.
Common Loan Covenants in Business Loans

In practice, various loan covenants exist that are commonly included in business loan agreements. These covenants are integral to maintaining a satisfactory level of accountability and assurance between parties involved. Understanding these covenants can help businesses navigate their obligations effectively.
Some of the most prevalent loan covenants include:
Failure to comply with these covenants may lead to complications ranging from increased interest rates to immediate default on the loan.
- Debt Service Coverage Ratio: Borrowers must maintain a specific ratio to ensure they can handle debt payments effectively.
- Current Ratio: This covenant requires the borrower to maintain a certain level of current assets in relation to current liabilities.
- Limit on Additional Debt: Borrowers agree to not incur additional debt without prior lender consent.
Awareness of these common covenants can provide businesses with a clearer understanding of their obligations, helping them avoid potential pitfalls.
The Impact of Breaking a Loan Covenant
Breaking a loan covenant can have dire consequences for businesses, potentially leading to severe financial repercussions. When a borrower violates a covenant, lenders may have the right to enforce remedies that could include raising interest rates, requiring immediate payment or even calling the loan due.
The consequences vary based on the terms of the covenant and the lender's policies. It is critical for borrowers to maintain open lines of communication with their lenders to mitigate the risks associated with breaking a covenant.
- Increased Interest Rates: Upon breaking a covenant, lenders may adjust the interest rates, making borrowing more expensive.
- Renegotiation: Lenders may demand terms to be renegotiated, which can lead to less favorable conditions for the borrower.
- Default: Serious breaches can result in immediate defaults, escalating the risk of bankruptcy or financial collapse.
Therefore, it is essential for businesses to proactively manage their compliance with loan covenants to safeguard their financial well-being.
Negotiating Loan Covenants

Negotiating loan covenants is a vital aspect of securing favorable lending terms for businesses. When engaging with lenders, borrowers should clearly outline their financial position and be open about their operational capabilities, ensuring that discussions about covenants reflect realistic expectations.
It's also prudent for borrowers to seek flexibility in terms of certain covenants. For instance, negotiating for grace periods or less restrictive operational covenants can provide a buffer against potential downturns in business performance.
- Communicate Clearly: Establish open dialogue with lenders regarding your business's unique circumstances and needs.
- Seek Flexibility: Aim to negotiate terms that allow for adjustments based on changing market conditions or business performance.
- Consult Professionals: Engage financial advisors or legal experts to guide negotiations to avoid unfavorable outcomes.
Successful negotiation of loan covenants ensures that businesses can operate efficiently while fulfilling their financial obligations.
Conclusion

In conclusion, loan covenants are indispensable in the realm of business loans, playing a critical role in ensuring financial stability and accountability. These agreements are beneficial to both lenders and borrowers, establishing a structured approach to financial obligations. By offering a safety net for lenders, they encourage better practices among borrowers while maintaining trust in borrowed funds.
Understanding the various types of loan covenants and their implications is vital for businesses navigating the often intricate landscape of financing. Proper management and negotiation of these covenants are key components that can have lasting impacts on a company's financial health.
Ultimately, by embracing the significance of loan covenants, businesses can promote a sustainable approach to growth and financial management, ensuring they remain in the good graces of their lenders while pursuing their strategic goals.














